Multiplexing : Introduction
- Multiplexing is a technique in which, multiple simultaneous analog or digital signals are transmitted across a single data link.
- The concept behind it is very simple: Proper Resource Sharing and its Utilization.
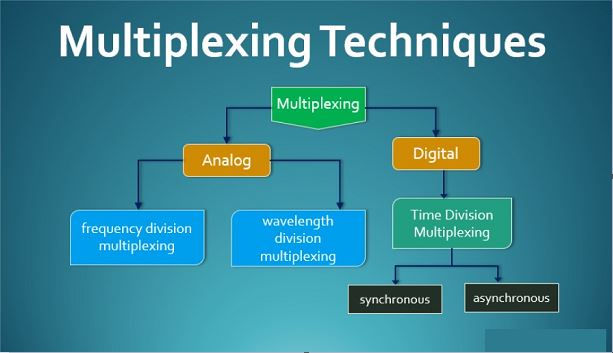
- It can be classified into four types. These are:

Multiplexing : Mobile Computing
Multiplexing : Frequency Division Multiplexing(FDM)
- In Frequency Division , the frequency dimension spectrum is split into bands of smaller frequency.
- FDM is used because of the fact that, a number of frequency band can work simultaneously without any time constraint.

Frequency Division
Advantages of FDM
- This concept is applicable on both analog signals as well as digital signals.
- Simultaneous signal transmission feature.
Disadvantages of FDM
- Less Flexibility.
- Bandwidth wastage is high and can be an issue.
For Example : Frequency Division Multiplexing can be used for radio station in a particular region as every radio station will have their own frequency and can work simultaneously without having any constraint of time.
Multiplexing : Time Division Multiplexing(TDM)
- Time Division is used for a particular amount of time in which the whole spectrum is used.
- Time frames of same intervals are made such that the entire frequency spectrum can be accessed at that time frame.

Time Division
Advantages of TDM
- Single user at a time.
- Less complex and more flexible architecture.
Disadvantages of TDM
- Difficult to implement.
For Example : ISDN(Integrated Service for Digital Network) telephonic service.
Multiplexing : Code Division Multiplexing(CDM)
- In Code Division Multiplexing, every channel is allotted with a unique code so that each of these channels can use the same spectrum simultaneously at same time.

Code Division
Advantages of CDM
- Highly Efficient.
- Less Inference.
Disadvantages of CDM
- Less data transmission rates.
- Complex in nature.
For Example : Cell Phone Spectrum Technology(2G, 3G etc.).
Multiplexing : Space Division Multiplexing(SDM)
- Space Division can be called as the combination of concepts of Frequency Division Multiplexing and Time Division Multiplexing.
- In SDM, the goal is to pass messages or data parallelly with the use of specific frequency at certain interval of time.
- It means, a particular channel for some amount of time will be used against a certain frequency band.
Advantages of SDM
- High Data transmission rate.
- Optimal Use of Time and Frequency bands.
Disadvantages of SDM
- Inference Problems.
- High inference losses.


Comments are closed