The Dynamic Source Routing protocol (DSR) is a simple and efficient routing protocol designed specifically for use in multi-hop wireless ad hoc networks of mobile nodes.
DSR allows the network to be completely self-organizing and self-configuring, without the need for any existing network infrastructure or administration.
It is a reactive protocol and all aspects of the protocol operate entirely on-demand basis. It works on the concept of source routing. Source routing is a routing technique in which
the sender of a packet determines the complete sequence of nodes through which, the packets are forwarded.
The advantage of source routing is : intermediate nodes do not need to maintain up to date routing information in order to route the packets they forward.
The protocol is composed of the two main mechanisms of “Route Discovery” and “Route Maintenance”.
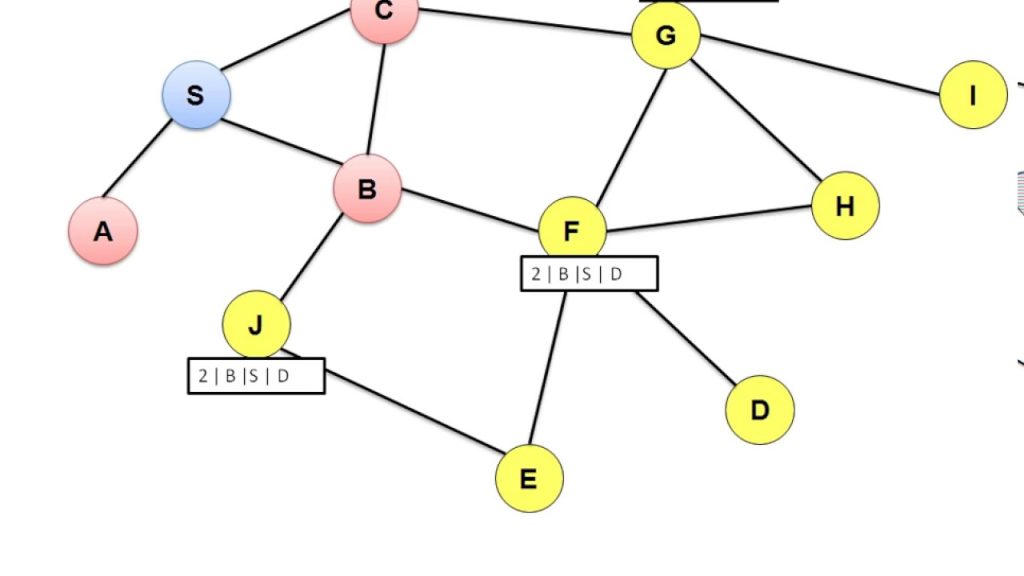
DSR requires each node to maintain a route – cache of all known self – to – destination pairs. If a node has a packet to send, it attempts to use this cache to deliver the packet.
If the destination does not exist in the cache, then a route discovery phase is initiated to discover a route to destination, by sending a route request.
This request includes the destination address, source address and a unique identification number.
If a route is available from the route – cache, but is not valid any more, a route maintenance procedure may be initiated.
A node processes the route request packet only if it has not previously processes the packet and its address is not present in the route cache.
A route reply is generated by the destination or by any of the intermediate nodes when it knows about how to reach the destination.
Example
In the following example, the route discovery procedure is shown where S1 is the source node and S7 is the destination node.

In this example, the destination S7, gets the request through two paths. It chooses one path based on the route records in the incoming packet and sends a reply using the reverse path to the source node. At each hop, the best route with minimum hop is stored. In this example, it is shown the route record status ate each hop to reach the destination from the source node. Here, the chosen route is S1-S2-S4-S5-S7.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
a) DSR uses a reactive approach which eliminates the need to periodically flood the network with table update messages which are required in a table-driven approach. The intermediate nodes also utilize the route cache information efficiently to reduce the control overhead.
b) The disadvantage of DSR is that the route maintenance mechanism does not locally repair a broken down link. The connection setup delay is higher than in table- driven protocols. Even though the protocol performs well in static and low-mobility environments, the performance degrades rapidly with increasing mobility. Also, considerable routing overhead is involved due to the source- routing mechanism employed in DSR. This routing overhead is directly proportional to the path length.