From Google Maps to Uber and Pokémon GO, GPS (Global Positioning System) has become an essential part of our daily lives. But how does your phone know exactly where you are? 🤔 Let’s break down the computer science, algorithms, and physics behind GPS navigation! 🚀📍
1. What is GPS? 🛰️🌍
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that determines your precise location anywhere on Earth.
✅ Developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1970s
✅ Works 24/7, in any weather, worldwide
✅ Used in smartphones, cars, aircraft, and military operations
💡 Fun Fact: GPS became available for civilian use in 1983 after a Korean Airlines plane accidentally entered Soviet airspace and was shot down.
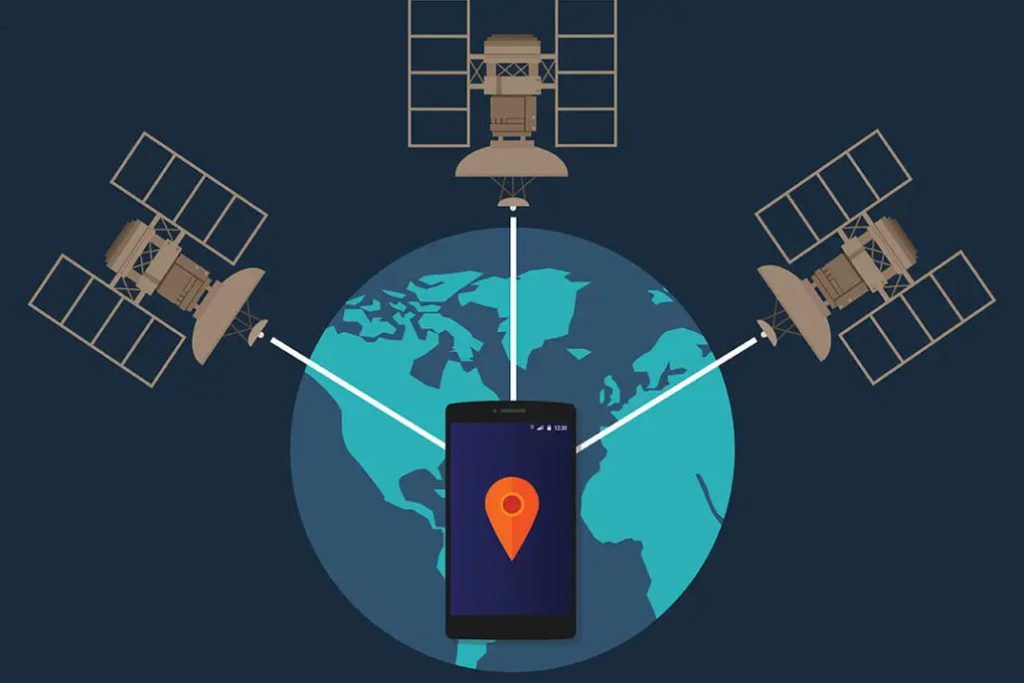
2. How Does GPS Determine Your Location? 📡📍
Your GPS device calculates your position using signals from satellites. Here’s how it works:
A. The Role of GPS Satellites 🛰️
🔹 24+ satellites orbit Earth, constantly sending signals
🔹 Each satellite broadcasts:
✅ Its position in space 🛤️
✅ A precise timestamp (when the signal was sent) ⏳
Your GPS receiver (phone, car, smartwatch) picks up these signals and uses triangulation to pinpoint your location.
B. Triangulation: Finding Your Exact Position 📍
GPS does not rely on one satellite—it needs at least three or four to work accurately.
🔸 Step 1: Your device receives signals from multiple satellites 🛰️🛰️🛰️
🔸 Step 2: It measures the time delay for each signal to arrive ⏳
🔸 Step 3: It calculates the distance to each satellite 📏
🔸 Step 4: Using these distances, it determines your exact latitude, longitude, and altitude 🌎
💡 Example: If your phone gets signals from three satellites, it can determine your 2D position (latitude & longitude). A fourth satellite is needed to calculate altitude (height above sea level).
3. The Computer Science Behind GPS: Algorithms & Data Processing 💻📊
A. Time Synchronization with Atomic Clocks ⏳⚛️
🔹 GPS satellites have atomic clocks that are accurate to nanoseconds (billionths of a second)
🔹 Your phone does not have an atomic clock, so it estimates time by comparing signals from multiple satellites
💡 Fun Fact: Without accounting for Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, GPS timing errors would cause a 10 km drift per day!
B. Signal Processing & Error Correction 🔄📡
GPS signals can be affected by:
❌ Atmospheric delays (signal distortion from air particles) 🌫️
❌ Multipath errors (signals bouncing off buildings) 🏙️
❌ Obstructions (trees, tunnels, mountains) 🌲⛰️
To improve accuracy, GPS systems use:
✅ Kalman Filters – Predicts and corrects location errors using past data 📈
✅ Differential GPS (DGPS) – Uses ground-based stations to improve accuracy 🔍
4. GPS Accuracy: How Precise Is It? 🎯
🔹 Smartphones GPS – 3 to 10 meters accuracy 📱
🔹 Military GPS – Centimeter-level accuracy 🎯
🔹 RTK GPS (Surveying & Drones) – 1-2 cm accuracy 🚁📏
💡 Upcoming Tech: Next-gen Quantum GPS could improve accuracy to millimeters! 🤯
5. Applications of GPS Beyond Navigation 🚀🌍
GPS is not just for maps—it powers many industries:
✅ Aviation & Shipping ✈️🚢 – Flight paths, autopilot, ship tracking
✅ Disaster Response 🚨 – Earthquake and tsunami monitoring
✅ Precision Farming 🚜 – Automated tractors and irrigation control
✅ Stock Market & Banking 🏦 – GPS timestamps financial transactions
✅ Space Exploration 🚀 – NASA uses GPS-like systems for spacecraft navigation
6. Future of GPS: What’s Next? 🔮
🔸 GPS III Satellites – Stronger, more resistant to jamming 📡
🔸 AI & Machine Learning – Predictive navigation and smarter routing 🤖
🔸 Quantum Navigation – GPS-free positioning using quantum mechanics ⚛️
🔸 Interplanetary GPS – Navigation systems for Mars & beyond 🪐
💡 Elon Musk’s Starlink may even provide GPS services in the future! 🚀📡
Conclusion: The Invisible Tech That Powers the World 🌍📡
GPS is a blend of physics, computer science, and satellite technology, enabling precise navigation, tracking, and data synchronization. As technology advances, GPS will become even more accurate, secure, and widespread—perhaps even guiding astronauts to Mars! 🚀🔭