comprises software (Web server and browser) and data (Web sites).
Internet Protocol (IP) Addresses:
– Every node has a unique numeric address
– Form: 32-bit binary number
– New standard, IPv6, has 128 bits (1998)
– Organizations are assigned groups of IPs for their computers
– Domain names
– Form: host-name. domain-names
– First domain is the smallest (Google)
– Last domain specifies the type of organization (.com)
– Fully qualified domain name – the host name and all of the domain names
– DNS servers – convert fully qualified domain names to IPs
HTTP:
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the communication protocol used by the Internet to transfer hypertext documents.
A protocol to transfer hypertext requests and information between servers and browsers
Hypertext is text, displayed on a computer, with references (hyperlinks) to
other text that the reader can immediately follow, usually by a mouse HTTP is behind every request for a web document or graph, every click of a hypertext link, and every submission of a form.
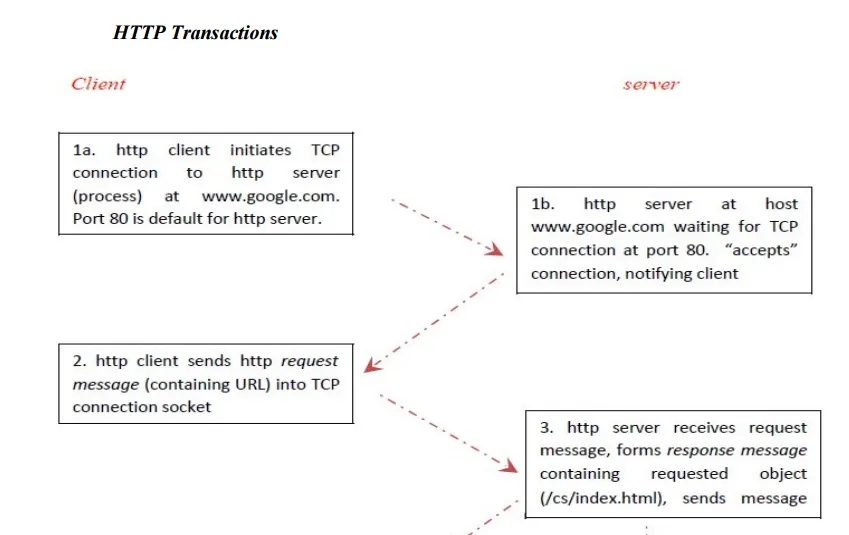
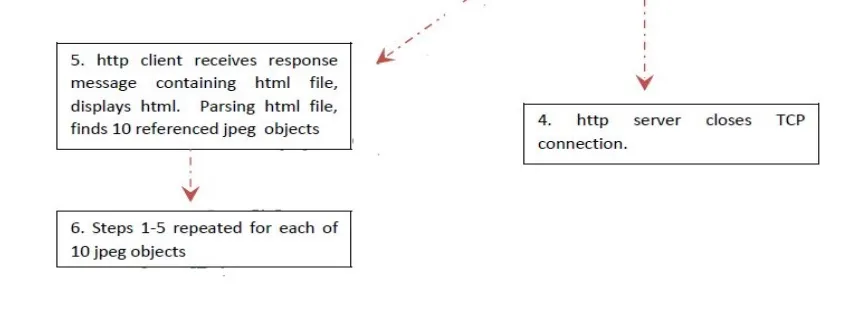
HTTP specifies how clients request data, and how servers respond to these requests.
The client makes a request for a given page and the server is responsible for finding it and returning it to the clie
The browser connects and requests a page from the server.
The server reads the page from the file system and sends it to the client and then terminates the connection
HTTP Transactions